DVT – Deep Vein Thrombosis
DVT – Deep Vein Thrombosis
January is DVT awareness month. Keystone Medical aims to join the fight against the morbidity and mortality resulting from DVT’s.
Here’s what you need to know:
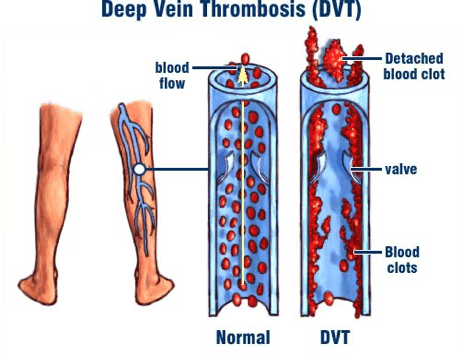
Blood clot formation is influenced by mainly three factors, namely hypercoagulability, stasis and endothelial injury, also known as Virchow’s Triad. The interaction of these factors can result in a clot (thrombus), leading to a blockage of blood flow within your veins. 1 When this occurs in a vein deep within the body, it is known as a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). Although this can occur throughout the body, it most often occurs in the lower leg, thigh or pelvis.
Risk factors for DVT formation include2:
- Trauma
- Surgery
- Prolonged Immobilization: Long hospital stays, paralysis, or sitting for long periods of time, such as driving or flying, resulting in decreased contraction of the muscles in the lower leg and slowing down of blood circulation
- Medical conditions causing hypercoagulability such as cancer, thrombophilia etc.
- Pregnancy
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)/oral contraceptive use
- Smoking affects blood circulation, leading to an increased risk
- Heart failure
- Family or personal history of clot formation or Pulmonary Emboli
Symptoms
Although deep vein thrombosis may occur without noticeable symptoms, the most common symptoms include2-3:
- Swelling of the affected leg.
- Pain (cramping and tenderness that often starts within the lower leg)
- Discoloured skin on the leg (reddish colour)
- Warm skin in the affected area
Symptoms in both legs are uncommon.
Complications of a DVT include:
- Recurrent DVT’s
- Varicose veins
- Chronic venous insufficiency
- Post Phlebotic Syndrome: permanent damage and scarring to the vein characterized by swelling, pain and skin pigmentation.
- Pulmonary Emboli: If the blood clot becomes dislodged, it can travel to the lungs, a life-threatening complication known as a pulmonary embolism and requires immediate medical attention. 3-4. These symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath with rapid breathing
- Constant chest pain and discomfort, worsened by deep inspiration
- Syncope (fainting)
- Rapid pulse
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a deep venous thrombosis includes a physical examination, blood tests (such as D-dimer) and the diagnostic modality of choice: an Ultrasound.
This study allows the Sonographer (Specialised technician performing the ultrasound), to monitor the blood flow in the veins from the pelvis to the foot, ensuring the overall flow of blood is not being constrained or restricted. Non-compressible veins or filling defects on doppler ultrasound are diagnostic of DVT.
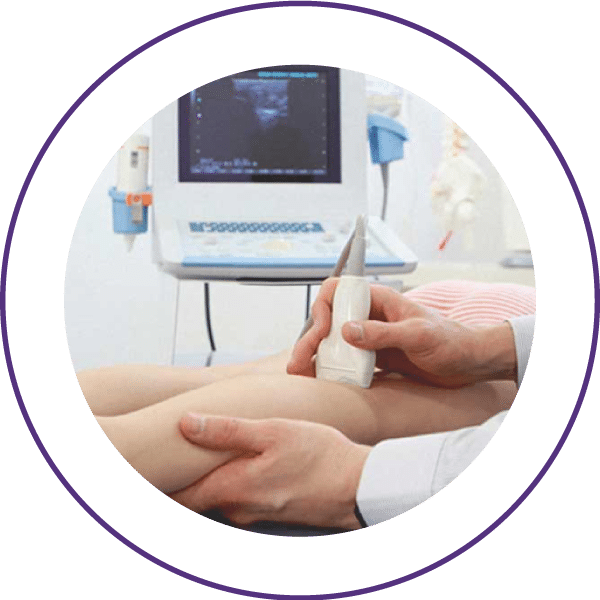
During the ultrasound examination, your legs will be exposed and ultrasound gel will be applied to your skin in a wide area. The gel is completely safe and painless. The ultrasound probe will then be moved over the gel on the surface of your leg. The gel serves as a bond between the skin surface and the ultrasound probe.
The probe uses sound waves that are then converted to images on a screen next to the bed. The procedure is painless and completed within a few minutes.
Depending on the clinical scenario and images, a treatment plan will be decided by your doctor. If the DVT is not an immediate threat, your doctor may request follow-up ultrasounds to monitor the progression of the clot.
Treatment of a deep vein thrombosis can vary, as the degree thereof is taken into consideration2-3. The most common treatment options include:
- Anticoagulant medication that manipulates the normal blood clotting process
- Compression stockings
- Surgery
Prevention2
- Avoid sitting still for long periods of time by moving regularly, especially on a long drive or flight.
- Loose-fitting clothing
- Lifestyle changes include plenty of fluids, a healthy diet and stopping smoking
- Weight loss and exercise
- Mechanical prevention includes compression stockings and air mattresses during a hospital stay
If you have any of the symptoms or risk factors highlighted in our article or have any questions regarding DVT’s, make your appointment for a diagnostic ultrasound at Keystone Medical today by via our website or phoning us at 087 055 0587.
Make a booking
Need to get an ultrasound done?
References
- Othieno R, Okpo E, Forster R. Home versus in-patient treatment for deep vein thrombosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018;.
- Deep vein thrombosis – Symptoms and causes [Internet]. Mayo Clinic. 2020 [cited 13 January 2020]. Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20352557
- Signs and Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis? [Internet]. Thrombosisadviser.com. 2020 [cited 13 January 2020]. Available from: https://www.thrombosisadviser.com/signs-symptoms-deep-vein-thrombosis/
- How is Deep Vein Thrombosis Diagnosed [Internet]. Thrombosisadviser.com. 2020 [cited 13 January 2020]. Available from: https://www.thrombosisadviser.com/how-is-deep-vein-thrombosis-diagnosed/